Fig. 11
Download original image
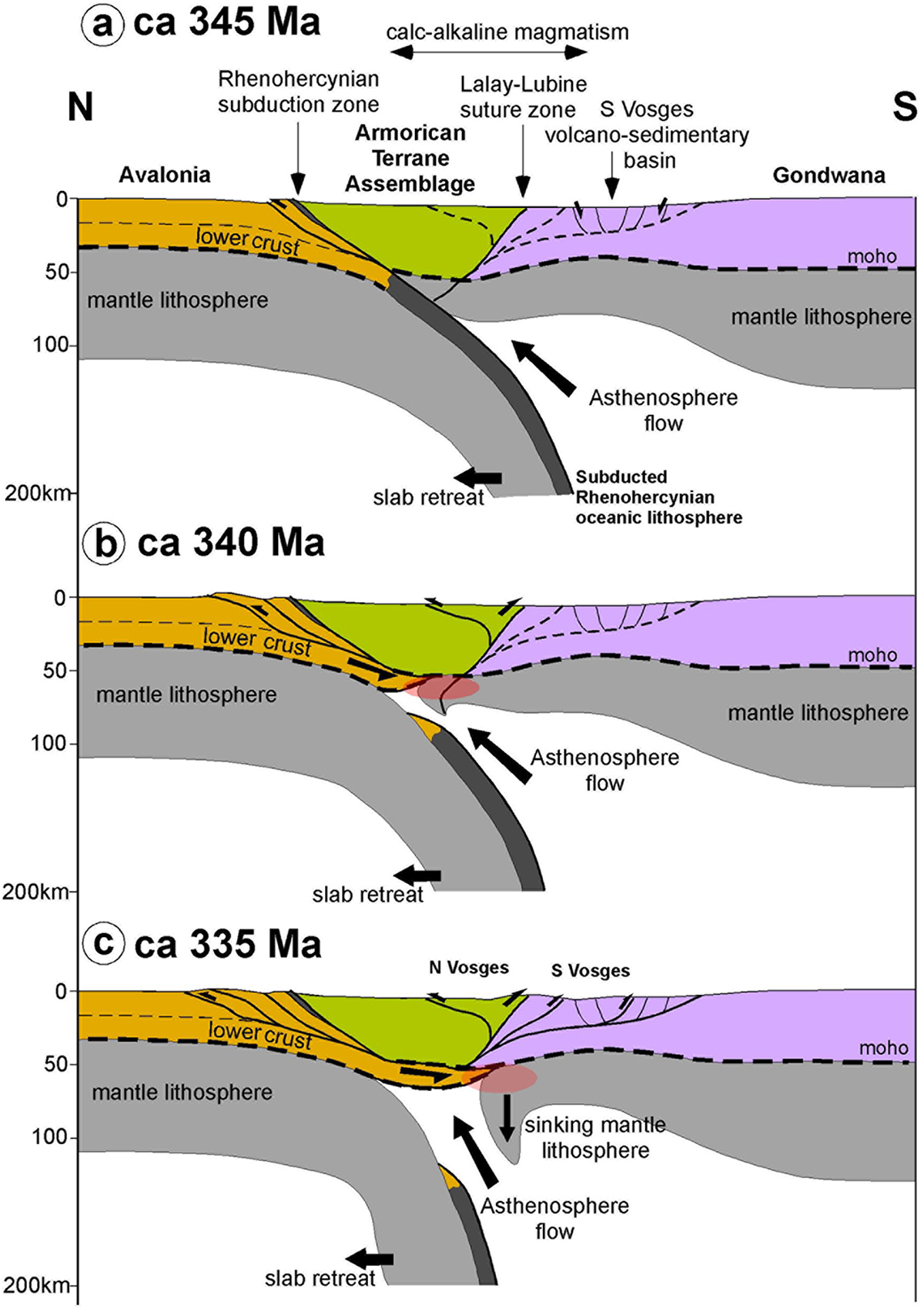
Sketch geodynamical model of the syn-collisional lithosphere delamination process proposed as the main driving mechanism for the development of the major ultra-potassic magmatic pulse in the Central-Southern Vosges at ca 340–335 Ma. a. ca 345 Ma stage: transition from oceanic to continental subduction along the Rhenohercynian trench; note the development of arc-type calc-alkaline magmatism forming the western extension of the Mid-German Crystalline Rise and back-arc extension localizing the Southern Vosges volcano-sedimentary basin. b. ca 340 Ma stage: onset of the colliding process and mantle lithosphere delamination; note the underthrusting of the Avalonian lower crust in between the Saxothuringian crust and mantle. The red zone refers to the possible zone of melting of the metasomatized mantle forming the initial source of the vaugnerites. c. ca 335 Ma stage: Southward (i.e. retro) propagation of thrusting within the Central-Southern Vosges massif and of the subcrustal delamination front with progressive sinking of the decoupled mantle lithosphere. Note the resultant parallel migration of the asthenospheric upwelling and of the associated melting zone of the metasomatized mantle (red zone).
Les statistiques affichées correspondent au cumul d'une part des vues des résumés de l'article et d'autre part des vues et téléchargements de l'article plein-texte (PDF, Full-HTML, ePub... selon les formats disponibles) sur la platefome Vision4Press.
Les statistiques sont disponibles avec un délai de 48 à 96 heures et sont mises à jour quotidiennement en semaine.
Le chargement des statistiques peut être long.




